PPE Detection and Compliance in Smart Environments
The potential of GNOSIS extends to a wider array of applications including Occupational Health and Safety in Smart Construction Environments. A crucial concept as Multimodal Knowledge Graphs for Smart Environments, which is the backend architecture for the system is effectively highlighted in Figure 1.
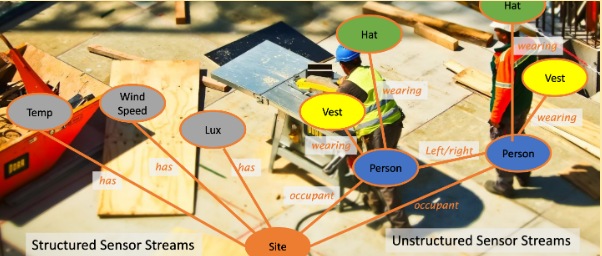
Figure 1: Construction Site highlighting relationships using Knowledge Graphs
The figure shows the connection between different sensors, objects and beings using knowledge graphs indicating the type of relationship between them. For example, a person object is related to a hat object using the relationship wearing. This type of functionality extends to different objects and relationships in the image, and are extremely useful in representing an event.
The OHS use cases and queries that will be looked at employ the concept of Video Event Knowledge Graphs (VEKG) to effectively determine various compliance scenarios, physical health being, and render positive results in a Smart Construction environment. Different safety guidelines have been issued by the health and safety regulatory authorities to prevent mishaps and construction hazards and accidents. Some of them are compliant with wearing hard hat PPE for the workers. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) states that 84% of all workers who suffered head injuries were not wearing head protection, which makes it all the way more crucial to cover this aspect of safety compliance.
The content services that these use cases employ which will make the understanding of the queries to follow, easier are highlighted well in Figure 2.
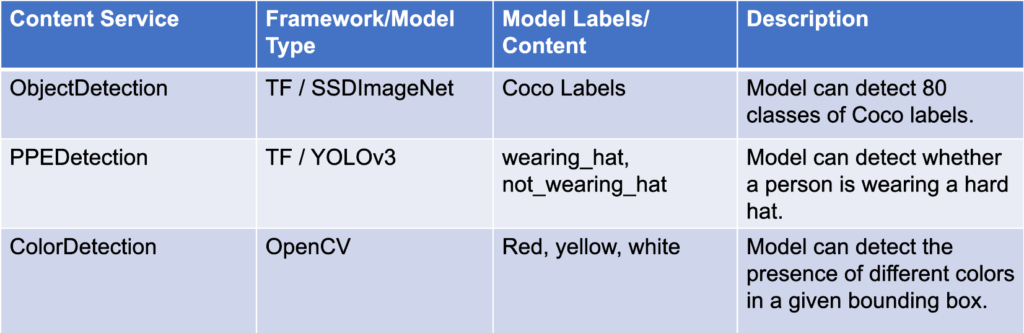
Figure 2: Content Services used in the OHS Use Cases
Use Case 1: Detect number of workers wearing a hard hat
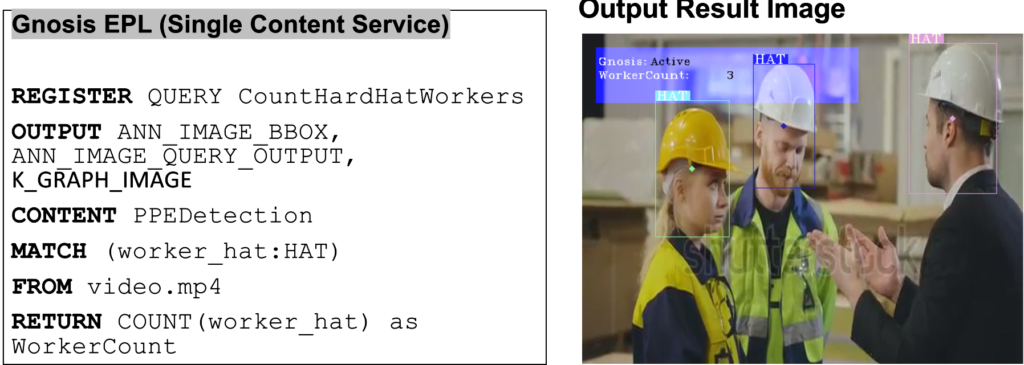
Figure 3: Use Case 1- Detect number of workers wearing a hard hat
The user wishes to count the number of workers wearing a hard hat. The query makes use of the PPEDetection content service to achieve the same which is supported by the video.
Use Case 2: Detect number of workers not wearing a hard hat
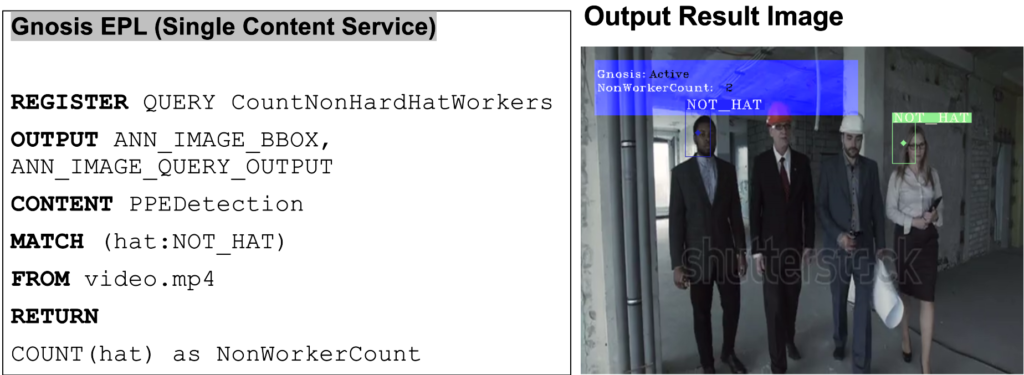
Figure 4: Use Case 2- Detect number of workers not wearing a hard hat
The user wishes to count the number of workers not wearing a hard hat. The query makes use of the PPEDetection content service to achieve the same.
Use Case 3: Detect number of workers wearing a white hard hat

Figure 5: Use Case 3- Detect number of workers wearing a white hard hat
The user wishes to count the number of workers wearing a white hard hat. This can be beneficial in situations where the grade/status of a worker is determined by the hat colour or to differentiate a visitor or a worker using the colour of the hat. The query makes use of the PPEDetection and ColorDetection content services to achieve the same.
Use Case 4: PPE Hard Hat Compliance

Figure 6: Use Case 4- PPE Hard Hat Compliance
The user wishes to count the number of workers wearing a white hard hat. This can be beneficial in situations where the grade/status of a worker is determined by the hat colour or to differentiate a visitor or a worker using the colour of the hat. The query makes use of the PPEDetection and ColorDetection content services to achieve the same.
Use Case 5: Count workers based on hat colour

Figure 7: Use Case 5- Count workers based on hat colour
The user wishes to count the number of workers wearing a hard hat based on the color of the hat. The query makes use of the PPEDetection, ColorDetection, ObjectDetection content services alongside a spatial operator to achieve the same. The spatial operator overlap_top ensures that the hat is being worn by the person and count operator counts the number of objects that qualify.
The current range of the system limits itself to hard hats and various scenarios for that compliance. However, this can be extended to different OHS situations in a smart construction site and also use cases using different streams like temperature, audio etc (work in progress) thereby including a wider array of aspects.